CHAPTER 3: Test Design Techniques- Kỹ thuật thiết kế test case (part 1)
3.1 The Test Development Process (K3)
During test analysis:
- The test basis documentation is analyzed in order to determine what to test, i.e., to identify the test conditions. – Trong quá trình phân tích test thì các tài liệu cơ sở của test được phân tích để xác định các trường hợp test, và các điều kiện test
- A test condition is defined as an item or event that could be verified by one or more test cases (e.g., a function, transaction, quality characteristic or structural element). – Một bộ điều kiện test được định nghĩa là 1 item hoặc sự kiện mà có thể kiểm tra được bởi 1 hoặc nhiều test case( vd chức năng, giao dịch, đặc tính chất lượng hoặc các yếu tố cấu trúc)
- Establishing traceability from test conditions back to the specifications and requirements enables both effective impact analysis when requirements change, and determining requirements coverage for a set of tests – Thiết lập ma trận theo dõi các điều kiện test với các đặc tả và yêu cầu sẽ giúp việc phân tích các ảnh hưởng hiểu quả hơn khi yêu cầu thay đổi và xác định được mức độ bao phủ của 1 tập hợp test
During test analysis and test design:
- The detailed test approach is implemented to select the test design techniques to use based on, among other considerations, the identified risks – Trong suốt quá trình phân tích các trường hợp test, kỹ thuật thiết kế test caces được lựa chọn sử dụng dựa trên sự xem xét phù hợp và các rủi ro
- The test cases and test data are created and specified. A test case consists of a set of input values, execution preconditions, expected results and execution post conditions, defined to cover a certain test objective(s) or test condition(s). – Một test case bao gồm 1 tập các giá trị đầu vào, điều kiện chạy, kết quả mong đợi, điều kiện sau khi chạy.
- The ‘Standard for Software Test Documentation’ (IEEE STD 829-1998) describes the content of test design specifications (containing test conditions) and test case specifications. – Thiết kế test cũng bao gồm cả việc tạo ra test cases và test data. – Tiêu chuẩn IEEE STD 829-1998 mô tả cụ thể 1 tài liệu thiết kế test case và đặc tả test case gồm những nội dung nào

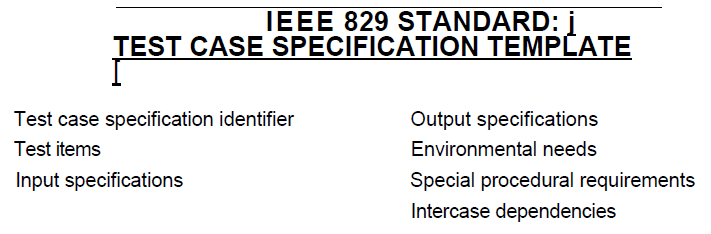
- Expected results should be produced as part of the specification of a test case and include outputs, changes to data and states, and any other consequences of the test. If expected results have not been defined, then a plausible, but erroneous, result may be interpreted as the correct one. Expected results should ideally be defined prior to test execution. Predict, oracle
- Expected results là 1 phần của đặc tả test case và bao gồm outputs, thay đổi về dữ liệu và trạng thái, và các kết quả khác của test. Nếu expected results ko được định nghĩa thì kết quả test sẽ ko được xác định chính xác ( Pass or faile) vì thế expected results nên đc định nghĩa trước khi chạy test
During test implementation
- The test cases are developed, implemented, prioritized and organized in the test procedure specification (IEEE STD 829-1998). – Trong quá trình thực hiện test thì test case sẽ được xây dựng, thực hiện, sắp xếp thứ tự ưu tiên, tổ chức trong tài liệu đặc tả thủ tục test (IEEE STD 829- 1998).
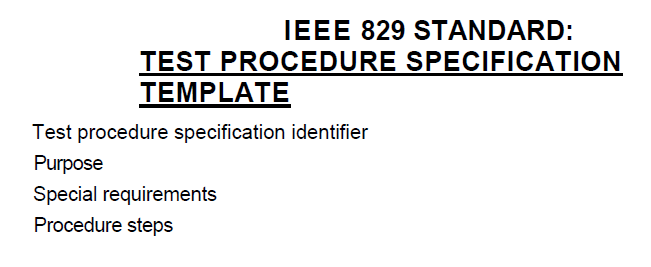
- The test procedure specifies the sequence of actions for the execution of a test. If tests are run using a test execution tool, the sequence of actions is specified in a test script (which is an automated test procedure). – Thủ tục test chỉ rõ thứ tự của các hành động dể thực hiện test. Nếu Nếu các Test này được chạy bằng tool, thì thứ tự các hành động sẽ được chỉ rõ trong test script.
3.2 Categories of Test Design Techniques
The purpose of a test design technique is to identify test conditions, test cases, and test data. – Mục tiêu của các kỹ thuật thiết kế test là để xấc định các điều kiện test, test cases, và test data
It is a classic distinction to denote test techniques as black-box or white-box – Chia thành 2 kỹ thuật thiết kế test cơ bản là black-box và white-box
- Black-box test design techniques (also called specification-based techniques) are a way to derive and select test conditions, test cases, or test data based on an analysis of the test basis documentation. This includes both functional and non-functional testing. Black-box testing, by definition, does not use any information regarding the internal structure of the component or system to be tested. – Kỹ thuật thiết kế Black-box test ( còn gọi là kỹ thuật hướng đặc tả) là cách dẫn xuất và lựa chọn các điều kiện test, TC, Test data dựa trên phân tích các tài liệu cơ sở của test. Nó bao gồm cả test function và non-function. Black-box test không cần sử dụng các thông tin liên quan đến cấu trúc bên trong của thành phần hay hệ thống.
- White-box test design techniques (also called structural or structure-based techniques) are based on an analysis of the structure of the component or system. – Kỹ thuật thiết kế White box test ( còn đc gọi là kỹ thuật hướng cấu trúc) là dựa trên sự phân tích cấu trúc của các thành phần hoặc hệ thống
- Black-box and white-box testing may also be combined with experience-based techniques to leverage the experience of developers, testers and users to determine what should be tested. – Kỹ thuật thiết kế test dựa trên kinh nghiệm có thể kết hợp cả 2 kỹ thuật Black box và white-box để tận dụng kinh nghiệm của LTV và tester, user để xác định cái gì cần test

Common characteristics of specification-based test design techniques include – Đặc điểm chung của kỹ thuật thiết kế test hướng đặc tả:
- Models, either formal or informal, are used for the specification of the problem to be solved, the software or its components
Các mô hình, hoặc là chính thức hay không chính thức, được sử dụng cho các đặc điểm kỹ thuật của vấn đề cần giải quyết, các phần mềm hoặc các thành phần của nó
- Test cases can be derived systematically from these models
TC được dẫn ra được bắt nguồn từ những mô hình có hệ thống
Common characteristics of structure-based test design techniques include – Đặc điểm chung của kỹ thuật thiết kế test hướng cấu trúc:
- Information about how the software is constructed is used to derive the test cases (e.g., code and detailed design information)
TC được dẫn ra dựa vào việc hiểu rõ cấu trúc của PM ( dự vào code hoặc thiết kế chi tiết)
- The extent of coverage of the software can be measured for existing test cases, and further test cases can be derived systematically to increase coverage
Mức độ bao phủ của test có thể đo đạc được và có thể bổ sung test case để tang được mức độ bao phủ này
Common characteristics of experience-based test design techniques include – Đặc điểm chung của kỹ thuật thiết kế test hướng kinh nghiệm:
- The knowledge and experience of people are used to derive the test cases – Kiến thức và kinh nghiệm của con người được dung để viết test cacse
- The knowledge of testers, developers, users and other stakeholders about the software, its usage and its environment is one source of information – Nguồn thông tin được lấy từ kiến thức của tester, LTV, user, nhà đầu tư về phần mềm, khả năng sử dụng và môi trường
- Knowledge about likely defects and their distribution is another source of information – Nguồn thông tin còn đc lấy từ các lỗi tương tự, sự phân bố của nó
Measurement – Đo đạc
Test successful coverage = Tổng TC Pass/ (Tổng TC- N/A)
- Objective assessment of thoroughness of testing (with respect to use of each technique)- Mục tiêu đánh giá mức độ triệt để của kiểm thử (mong đợi đối với mỗi kỹ thuật được sử dụng)
- Useful for comparison of one test effort to another – Sử dụng để so sánh nỗ lực của một thử nghiệm với những cái khác
- Eg:
| Project A | Project B |
| 60% Equivalence partitions – phân vùng tương đương | 40% Equivalence partitions |
| 50% Boundaries – biên | 45% Boundaries |
| 75% Branches – nhánh | 60% Branches |

Leave a comment